
- Applications
-
Products
-
Liquid Handling
- firefly Accelerate genomic research with innovative all-in-one, compact liquid handling
- mosquito Nanolitre liquid handling technology performs ‘traditional’ tasks at a fraction of the volume, and higher speeds
- dragonfly Delivers accurate and repeatable nanolitre to milliliter dispensing
- apricot Automated liquid handling instrumentation for convenient general use across your entire team
- Sample Preparation
-
Sample Management
- comPOUND A scalable, reliable, and secure compound management solution
- BioMicroLab Easy-to-use sample management automation instruments
- arktic Robust biospecimen storage and management down to -80°C
- lab2lab Novel sample and data transfer network system
- comPACT Reliable and efficient -20°C storage and retrieval has never been more accessible
-
Liquid Handling
-
About
- Company With a focus on liquid handling, sample preparation and sample management, our expert teams create state-of-the-art solutions that scientists and researchers can trust Culture We have one overarching mission: to work together to accelerate life science research. Through our innovative solutions and state-of-the-art tools, we believe we can make a real difference to human health Partners Collaboration is key in our mission to make a real difference to human health. Partnering with application leaders globally, we co-create to solve new challenges across the life sciences. Innovation From the initial prototype through to manufacturing, installation and beyond, we bring a problem-solving mindset and technical expertise to drive innovation
-
Executive Leadership
 Through strategic guidance, visionary thinking, and a relentless pursuit of excellence, our senior executives steer SPT Labtech towards achieving its mission of making a real difference to human health through solving advanced laboratory challenges.
Learn more
Through strategic guidance, visionary thinking, and a relentless pursuit of excellence, our senior executives steer SPT Labtech towards achieving its mission of making a real difference to human health through solving advanced laboratory challenges.
Learn more 
-
View all
 Board of Directors
Board of Directors
 Our Board of Directors are committed to driving the long-term success and sustainability of SPT Labtech, providing expert guidance and oversight to execute the company’s ambitious commercial strategy.
Learn more
Our Board of Directors are committed to driving the long-term success and sustainability of SPT Labtech, providing expert guidance and oversight to execute the company’s ambitious commercial strategy.
Learn more 
-
Knowledge Base
- Resources Our wide range of insightful resources include videos, whitepapers, eBooks, application notes and more Events & Webinars Meet the SPT team at events all over the globe and virtually via our webinars Podcast We chat with innovators and leaders from across the community to gain their unique insights. News Latest news from SPT Labtech globally Blog Our latest blog posts feature trends in research, innovative techniques and new technology
-
08 October, 2025
 SPT Labtech and Agilent Introduce Automated Target Enrichment Protocols for Genomic Workflows
Continue reading
SPT Labtech and Agilent Introduce Automated Target Enrichment Protocols for Genomic Workflows
Continue reading 
-
22 September, 2025
 How Novartis Is Shaping the Future of Lab Automation Through Smart Sample Transport
Continue reading
How Novartis Is Shaping the Future of Lab Automation Through Smart Sample Transport
Continue reading 
-
09 July, 2025
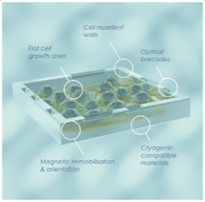 SPT Labtech and Semarion Collaborate to Advance Automated Cell-Based Assay Workflows
Continue reading
SPT Labtech and Semarion Collaborate to Advance Automated Cell-Based Assay Workflows
Continue reading 
10
- Careers
- Home
- Resources
Resources
Explore insightful resources that include videos, whitepapers, eBooks, application notes and more
- 3D Cell Culture
- Assay Setup
- Automated Assay Development
- Biostorage and Biobanking
- Chemical Crystallization
- Compound Management
- CryoEM
- Crystal Screen Optimization
- DNA Normalization
- DNA Quantification
- Hanging Drop Crystallization
- High Throughput Screening
- Lipidic Cubic Phase (in meso)
- Magnetic Bead Clean-up
- Medicinal Chemistry
- NGS Library Prep
- PCR and qPCR
- Protein Crystallography
- Reformat
- Sample Tracking
- Single Cell Genomics
- Single Particle Analysis
- Sitting Drop Crystallization
- Synthetic Biology
- Transcriptomics
- Tube Cap/Decap
- Tube Labeling
Explore our flyer for mosquito and its use in nanoscale synthesis and how it is advancing chemistry with ultra-low volume reactions.
Read moreExplore our flyer on compound screening and validation with mosquito® and how to reduce assay costs without compromising performance
Read moreDownload our latest flyer to explore our dynamic duo for low-volume liquid handling for genomics. Explore the mosquito® and dragonfly® increases your productivity and reduces the cost per sample by miniaturizing your NGS method with proven workflow solutions for over 40 NGS kits, including industry standards such as Illumina Nextera XT, Illumina DNA Prep, NEBNext Ultra II, plus many more.
Read moreDownload our latest flyer for the mosquito® X1 to discover the key benefits and how it achieves high speed low volume cherry picking.
Read moreDownload our latest flyer for the mosquito® HV to discover the key benefits and how it is bridging the nanolitre to microlitre gap.
Read moreDownload our latest flyer for the mosquito® Gen3 to explore its key benefits and how it is lowering the barrier to NGS miniaturization.
Read moreExplore our latest flyer for the mosquito® LV to discover the key benefits and how it is making high throughput assay miniaturization simple.
Read moreIn this webinar, learn how the team at Artios Pharma have developed and implemented automated end-to-end workflows for sample storage and tracking, processing, assay-ready plate generation and sample mapping for analysis, using Titian Sample Bank software and SPT Labtech automation systems. Using this compound management workflow, they have demonstrated up to a 40% reduction in data posting cycle times and decreased running costs, as well as using the system for clinical sample supply and tracking, all of which results in quicker data reporting to drive decision making and more effective use of resources.
Read moreIntroducing our most compact and accessible member of the mosquito family. mosquito Gen3 offers highly accurate and precise multi-channel pipetting from 500 nL to 5 µL, allowing genomics researchers to benefit from miniaturization across a range of applications, irrespective of liquid class. The instrument’s rapid plate-to-plate pipetting motion and tip exchange maximize speed and efficiency.
Read moreThis application note highlights how mosquito HV genomics has been used to automate the Illumina Nextera XT protocol at SEQ-IT, achieving 5X miniaturized reaction volumes while delivering reproducible, high-quality libraries. Based in Kaiserslautern in Germany, SEQ-IT is a mid-sized company offering both Sanger sequencing and NGS services.
Read moreThis poster highlights how mosquito HV genomics has been used to automate the Illumina Nextera XT protocol at SEQ-IT, achieving 5X miniaturized reaction volumes while delivering reproducible, high-quality libraries. This miniaturized method was developed to identify and screen mutations with oncogenic potential and drug resistance (HIV, HBV, HCV), SNP detection, as well as in HLA-typing, among other applications.
Read moreUsing dedicated software and automation, Artios have developed in-house compound management for Design-Make-Test-Analyze processing and assay-ready plate generation. This results in: - Increased sample and data integrity through audited and trackable processes - Reduced cycle times and cost - Faster data reporting for better decision making and use of resources
Read more
