
- Applications
-
Products
-
Liquid Handling
- firefly Accelerate genomic research with innovative all-in-one, compact liquid handling
- mosquito Nanolitre liquid handling technology performs ‘traditional’ tasks at a fraction of the volume, and higher speeds
- dragonfly Delivers accurate and repeatable nanolitre to milliliter dispensing
- apricot Automated liquid handling instrumentation for convenient general use across your entire team
- Sample Preparation
-
Sample Management
- comPOUND A scalable, reliable, and secure compound management solution
- BioMicroLab Easy-to-use sample management automation instruments
- arktic Robust biospecimen storage and management down to -80°C
- lab2lab Novel sample and data transfer network system
- comPACT Reliable and efficient -20°C storage and retrieval has never been more accessible
-
Liquid Handling
-
About
- Company With a focus on liquid handling, sample preparation and sample management, our expert teams create state-of-the-art solutions that scientists and researchers can trust Culture We have one overarching mission: to work together to accelerate life science research. Through our innovative solutions and state-of-the-art tools, we believe we can make a real difference to human health Partners Collaboration is key in our mission to make a real difference to human health. Partnering with application leaders globally, we co-create to solve new challenges across the life sciences. Innovation From the initial prototype through to manufacturing, installation and beyond, we bring a problem-solving mindset and technical expertise to drive innovation
-
Executive Leadership
 Through strategic guidance, visionary thinking, and a relentless pursuit of excellence, our senior executives steer SPT Labtech towards achieving its mission of making a real difference to human health through solving advanced laboratory challenges.
Learn more
Through strategic guidance, visionary thinking, and a relentless pursuit of excellence, our senior executives steer SPT Labtech towards achieving its mission of making a real difference to human health through solving advanced laboratory challenges.
Learn more 
-
View all
 Board of Directors
Board of Directors
 Our Board of Directors are committed to driving the long-term success and sustainability of SPT Labtech, providing expert guidance and oversight to execute the company’s ambitious commercial strategy.
Learn more
Our Board of Directors are committed to driving the long-term success and sustainability of SPT Labtech, providing expert guidance and oversight to execute the company’s ambitious commercial strategy.
Learn more 
-
Knowledge Base
- Resources Our wide range of insightful resources include videos, whitepapers, eBooks, application notes and more Events & Webinars Meet the SPT team at events all over the globe and virtually via our webinars Podcast We chat with innovators and leaders from across the community to gain their unique insights. News Latest news from SPT Labtech globally Blog Our latest blog posts feature trends in research, innovative techniques and new technology
-
11 December, 2025
 5 Key Sample Management Automation Trends for 2025- 2026: An Interview with SPT Labtech’s Cory Tiller
Continue reading
5 Key Sample Management Automation Trends for 2025- 2026: An Interview with SPT Labtech’s Cory Tiller
Continue reading 
-
04 December, 2025
.jpg?length=320&name=SBTi%20Target%20Announcement,%20mktg%20(1200%20x%20800%20px).jpg) Delivering Sustainable Science: SPT Labtech Validates GHG Reduction Targets to Meet Customer Needs
Continue reading
Delivering Sustainable Science: SPT Labtech Validates GHG Reduction Targets to Meet Customer Needs
Continue reading 
-
20 November, 2025
 SPT Labtech enables automated PacBio Kinnex full-length RNA-seq library preparation workflow on SPT’s firefly platform
Continue reading
SPT Labtech enables automated PacBio Kinnex full-length RNA-seq library preparation workflow on SPT’s firefly platform
Continue reading 
10
- Careers
- Home
- Drug Discovery
- DNA-Encoded Library (DEL) Screening
DNA-Encoded Library (DEL) Screening
DNA-encoded library (DEL) screening has emerged as a transformative technique in drug discovery, revolutionizing the way researchers identify potential therapeutic compounds.
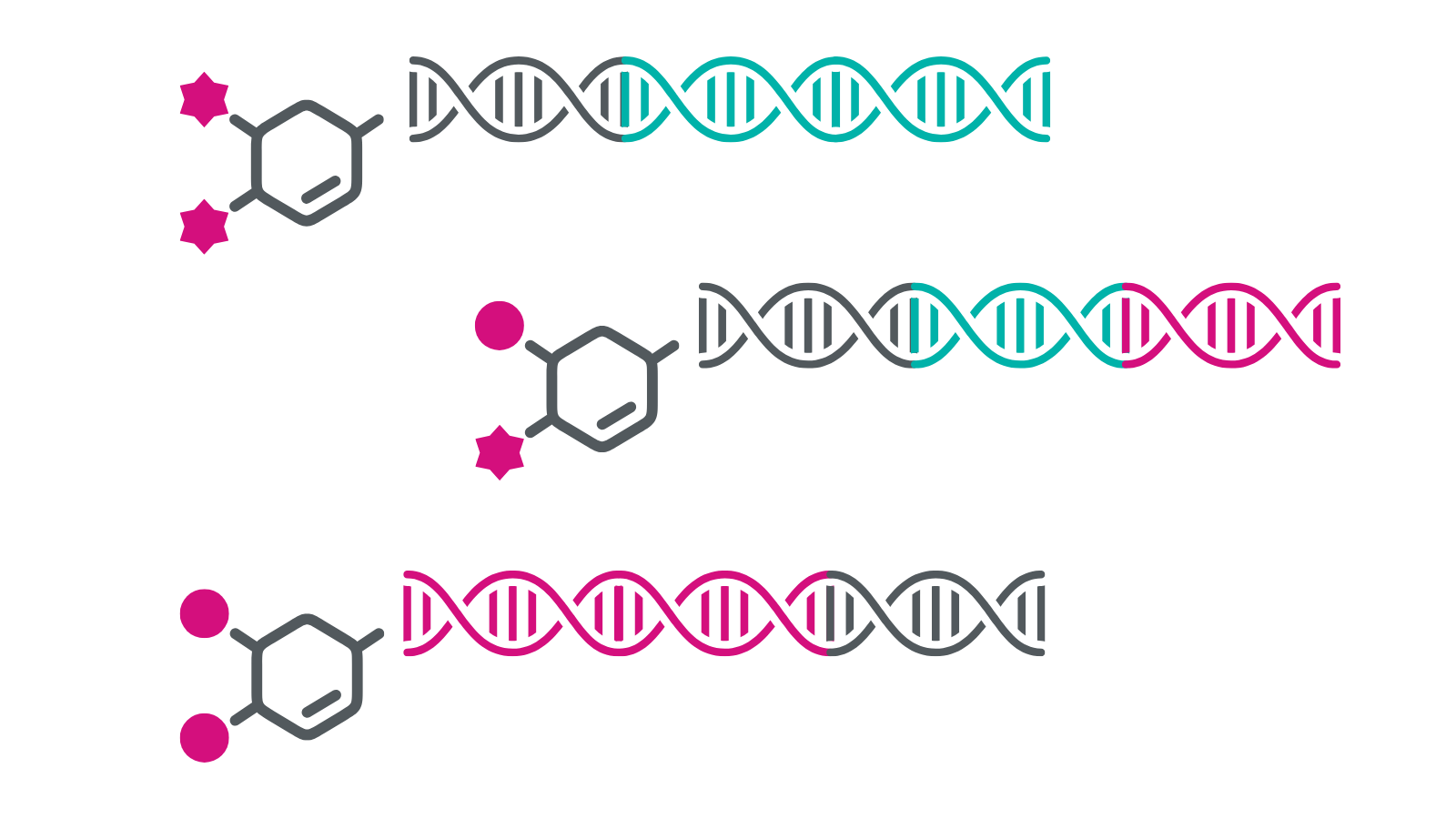
Introduction to DEL screening
DNA-encoded library (DEL) screening has emerged as a transformative technique in drug discovery, revolutionizing the way researchers identify potential therapeutic compounds. The technique involves synthesizing vast libraries of small molecules, each tagged with a unique DNA sequence that acts as a molecular barcode. These libraries can then be screened against a target protein to identify promising drug candidates efficiently and cost-effectively.
Enhancing drug discovery with DEL screening
High-throughput screening is a cornerstone of early-phase drug discovery, allowing the rapid identification of potential hit compounds. However, the costs associated with traditional chemical libraries can be as high as $1 billion USD, meaning this approach can quickly become expensive and resource intensive.
DNA-encoded libraries (DELs) offer a powerful and cost-effective alternative to traditional high-throughput screening (HTS) methods. These consist of compounds linked to unique DNA barcodes, allowing for the simultaneous screening of vast compound libraries through affinity selection. In this process, compounds that bind to target molecules are enriched, and their DNA tags are sequenced for identification.
This method allows millions of compounds to be tested in a single tube, vastly increasing the scale and efficiency of screening compared to traditional HTS, which typically involves individual compounds in 384 or 1536-well microplates. Furthermore, affinity selection workflows are highly amenable to automated liquid handling technologies to ensure their throughput, reliability and data quality.

Understanding the DEL screening workflow
A typical DEL screening workflow allows researchers to screen vast libraries of small molecules quickly and efficiently.

- A diverse library of small molecules is synthesized through combinatorial chemistry, with each step including the addition of a DNA sequence that builds a unique barcode identifier.
- The encoded libraries are incubated with the target protein. Non-binding ligands are removed through washing, ensuring that only specific binders remain.
- Bound molecules are eluted, and their DNA is amplified. Sequencing then identifies the hits from the screening.
The remaining steps then follow the typical drug discovery pathway. Hits are synthesized and validated independently to confirm their binding affinity and biological activity. The most promising candidates undergo optimization to enhance potency, selectivity, and pharmacokinetic properties, followed by preclinical and clinical testing.
The role of automation in DEL screening
Multiple steps the workflow involve manual pipetting steps and are therefore prime candidates for automated liquid handling:
- Increased throughput: Automation enables the parallel synthesis of vast chemical libraries, significantly boosting throughput while reducing manual errors.
- Streamlined screening: Automated systems can manage incubation, washing, and elution steps with precision, ensuring high-throughput and consistent data quality.
- Enhanced NGS preparation: Automating PCR setup and DNA preparation for NGS sequencing allows for the accurate handling of small volumes, increasing speed and accuracy beyond what is possible manually.
- Accelerated validation: Automation also speeds up downstream validation assays, making the overall process more efficient.
For drug discovery labs, incorporating automation into DEL screening workflows means faster identification of promising candidates, more reliable results, and the ability to handle larger and more complex projects, ultimately accelerating the overall discovery process.
firefly®
Our all-in-one platform brings together multiple technologies within a single compact design, including non-contact dispensing, 96/384-well pipetting, shaking and temperature controlled incubation. Underpinned by powerful, intuitive software, firefly unlocks the potential of automation for all to accelerate genomics and drug discovery workflows.
Explore firefly

firefly+®
firefly+ expands on the current liquid handling capabilities of firefly with an integrated thermocycler and additional labware capability, all while maintaining our commitment to usability and compact design. These additions facilitate longer hands-free workflows for increased .lab efficiency.
Explore firefly+mosquito® HV genomics
mosquito ® HV genomics offers highly accurate and precise multi-channel pipetting from 500 nL to 5 µL allowing researchers to benefit from miniaturization across a range of applications, irrespective of liquid class. The instrument’s pre-sterilized disposable pipettes eliminate cross-contamination and maintain data integrity while the rapid plate-to-plate pipetting motion and tip exchange maximize speed and efficiency.
Explore mosquito

dragonfly® discovery
Multi-channel non-contact dispensing from positive displacement syringes. The dragonfly product range delivers accurate and repeatable nanoliter to milliliter dispensing, every time, irrespective of liquid viscosity or environmental conditions.
Explore dragonflyConclusion
DNA-encoded library (DEL) screening is a powerful tool in the arsenal of drug discovery, offering unparalleled efficiency and accuracy in identifying potential therapeutic compounds. While the technique presents certain challenges, innovations in liquid handling solutions, such as SPT Labtech's firefly and firefly+, provide effective solutions that streamline workflows and enhance the overall efficiency of DEL screening. By leveraging these advanced technologies, researchers can unlock the full potential of DEL screening, accelerating the discovery of new drugs and ultimately improving patient outcomes.
Key Resources
Poster ➤➤➤
01.
Accelerating Drug Discovery at Totus Medicines: DNA-Encoded Library Screening with firefly®
Totus Medicines has developed a platform capable of identifying covalent small molecule ligands via high-throughput cell-based DEL screening. This poster outlines how the team is streamlining hit identification, optimization, and technology development, to accelerate the discovery of novel therapeutic candidates using our firefly automated liquid handling platform. We present the metrics that have been collected over one year of screening using Totus Medicine’s proprietary covalent DELs to run over 2000 unique selections against a large number of targets, spanning diverse therapeutic areas.

Webinar ➤➤➤
02.
Accelerate small molecule lead discovery with automated multichannel pipetting and DEL technology
When utilizing screening methods such as DEL technology, follow-up hit validation must be performed using traditional biochemical assays.
In this webinar, the team from X-Chem reviews the use of mosquito LV to accelerate early-stage small molecule lead discovery through the lens of Hydroxyacid oxidase 1 (HAO1).

Application Note ➤➤➤
03.
mosquito® LV: An assay's best friend
After a successful DEL screen, it is essential to have access to a high-throughput method of assaying compounds to validate hits. Learn how mosquito LV's positive displacement nanoliter pipetting has improved the way that X-Chem work with off-DNA compounds synthesized from DELcore and DELflex collaborations.


